Experiencing increased hair growth after laser hair removal might feel ironic and frustrating—especially since the procedure is designed explicitly to eliminate unwanted hair. For those who encounter this paradox, questions about effectiveness, safety, and proper methods naturally arise. Instead of just another overview, this article directly addresses why hair sometimes grows more intensely after laser hair removal, what paradoxical hypertrichosis means for your hair removal journey, and how you can manage or even reverse this unusual outcome.
Can Laser Hair Removal Cause More Hair Growth?
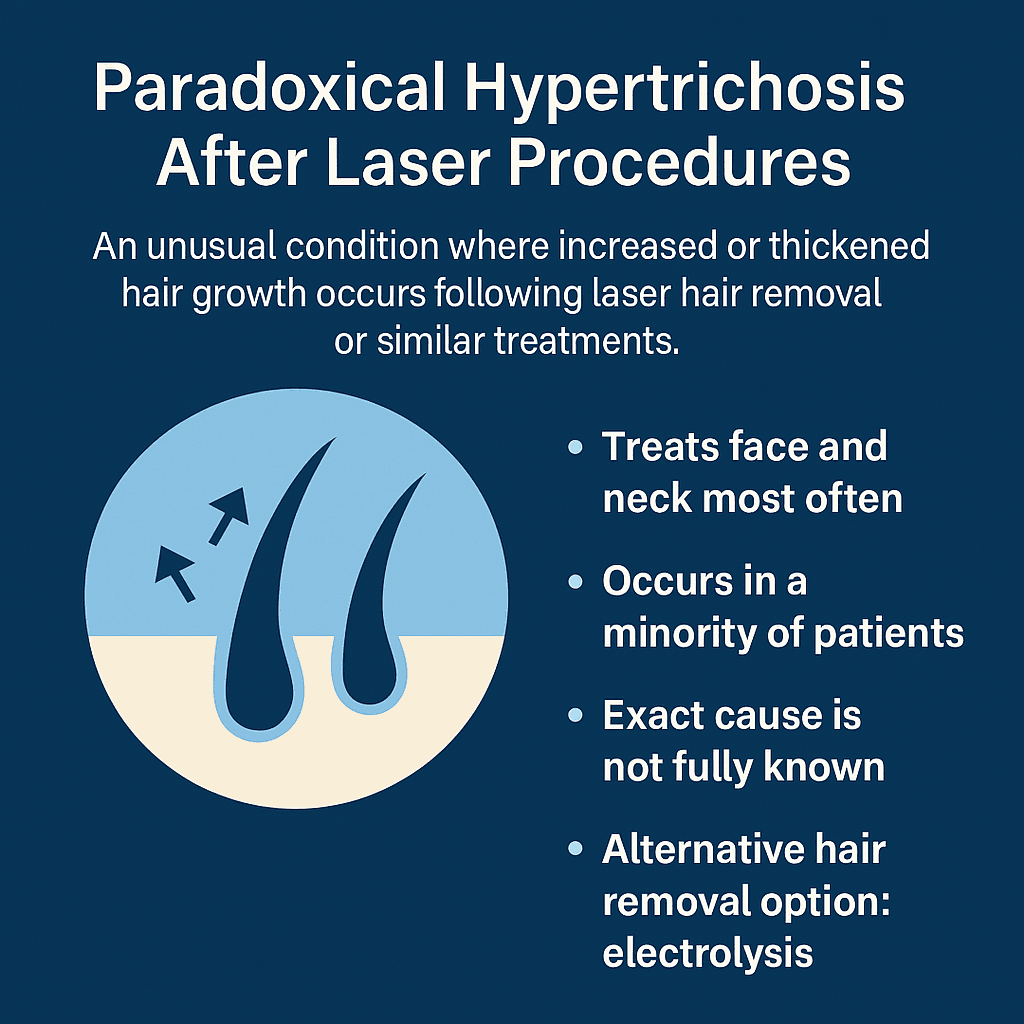
Laser hair removal is commonly chosen for its promise of long-term hair reduction, yet a small percentage of individuals experience the opposite effect—unexpected hair growth. This counterintuitive response is known as paradoxical hypertrichosis, a rare side effect where treated areas (or nearby untreated areas) begin to grow thicker, darker, and more visible hair after multiple sessions. This phenomenon often occurs in areas with finer or vellus hair, such as the face or neck, and is more likely in people with darker skin tones or those with underlying hormonal imbalances. Recognizing early indicators can help prevent continued stimulation of unwanted hair and guide corrective actions.
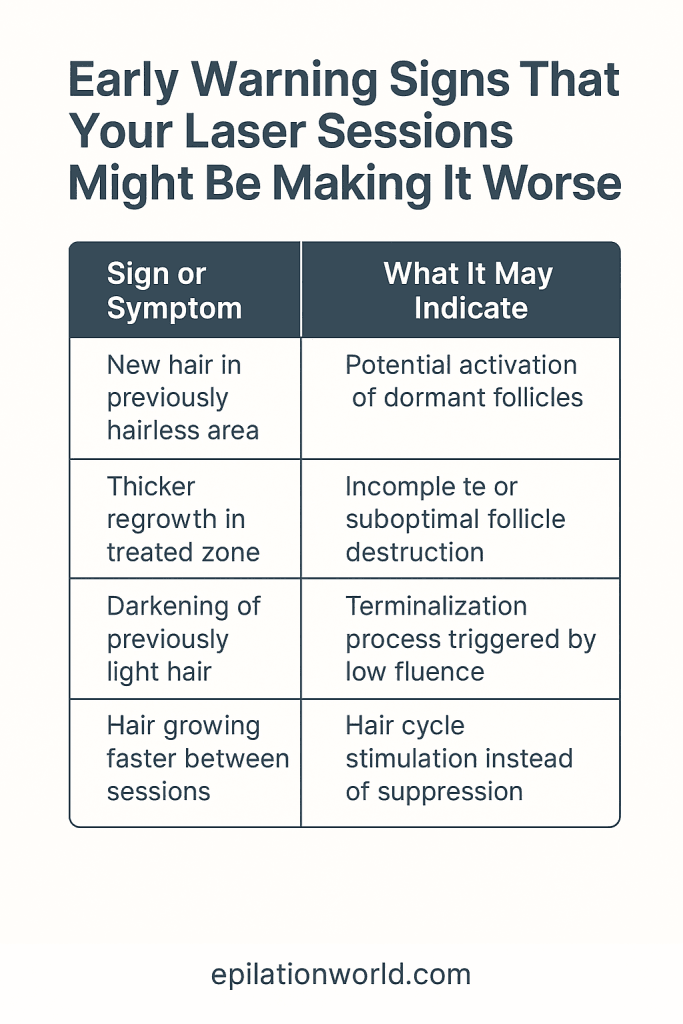
Early Warning Signs That Your Laser Sessions Might Be Making It Worse
Some of the early warning signs that your laser hair removal might be causing unintended hair growth include:
- The appearance of new hair in areas that were previously hairless: This could suggest that dormant follicles have been activated by subtherapeutic laser exposure.
- Thicker or denser regrowth in treated zones: When the energy level is too low, it may only partially affect the hair follicle, leading to incomplete destruction and unexpected regrowth.
- Previously light or fine hairs becoming darker and coarser: This is often the result of terminalization, a process in which vellus hairs convert to terminal hairs due to insufficient laser fluence.
- Hair growing faster between sessions than before treatment began: This may be due to follicular stimulation instead of suppression, especially when laser parameters are not optimized for your hair and skin type.
While such cases are rare, they are a real possibility—especially when non-FDA-approved devices, inexperienced operators, or incorrect energy settings are involved. Ensuring your treatment is suited to your hair and skin type is essential for optimal results and safety.
Additionally, although laser hair removal is often considered a permanent solution, its long-term effectiveness can vary based on hormonal health, hair color, and the laser technology used. To better understand expected outcomes and longevity, visit our detailed guide on how permanent laser hair removal really is.
What Is Paradoxical Hypertrichosis?
Paradoxical hypertrichosis is an unusual side effect of laser or IPL (Intense Pulsed Light) procedures, characterized by an increase in hair growth rather than its reduction. Typically occurring in areas such as the face, neck, shoulders, or upper arms, this condition affects individuals with finer or lighter hair more frequently but can potentially impact anyone.
For those interested in a deeper understanding of paradoxical hypertrichosis, the detailed scientific review titled Paradoxical Hypertrichosis After Laser Therapy: A Review thoroughly investigates potential causes, risk factors, laser types involved, and effective management strategies. This comprehensive analysis, authored by respected dermatologists, provides valuable insights backed by clinical studies and real-world cases, making it an excellent resource for individuals, professionals, or anyone seeking reliable and scientific explanations regarding this unusual condition.
Why Does Hair Growth Increase After Laser Procedures?
Although laser hair removal is widely regarded as a reliable method for long-term hair reduction, several underlying factors can unexpectedly lead to increased hair growth in some individuals. Understanding the reasons behind this paradox is essential to avoid ineffective outcomes and to choose the right treatment approach. From device settings to individual biological traits, the following sections break down the most common contributors to this rare but frustrating experience.
Incorrect Laser Device and Settings
Using an inappropriate laser type or incorrect settings can stimulate hair follicles rather than destroying them. Lower energy levels might partially warm follicles without effectively disabling them, thereby stimulating growth instead.
Hair Type and Skin Tone Factors
Individuals with lighter, finer hairs or darker skin tones are more susceptible to paradoxical hypertrichosis. In these cases, the laser energy is insufficiently absorbed, causing stimulation of hair follicles into a growth phase rather than disabling them. Interestingly, individuals with red or very light-colored hair face additional challenges with laser responsiveness due to lower melanin levels. This topic is explored further in our guide on how effective laser hair removal is on red hair.
Hormonal Imbalances (e.g., PCOS)
Hormonal conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can independently cause excessive hair growth, complicating the outcomes of laser procedures. Individuals with underlying hormonal conditions may experience paradoxical effects more frequently. Recent research highlights the effectiveness of laser therapies combined with systemic treatments in managing PCOS-related hair growth. For more detailed information, you can review the systematic study published by JAMA Dermatology titled Laser and Light-Based Therapies for Hirsutism Management in Women With PCOS.
Hormonal conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can independently cause excessive hair growth, complicating the outcomes of laser procedures. Individuals with underlying hormonal conditions may experience paradoxical effects more frequently.
Does Laser Hair Removal on the Face Cause More Hair?
The facial area is particularly sensitive when it comes to laser hair removal—not just due to skin delicacy, but also because of the high concentration of vellus hairs, commonly known as peach fuzz. These fine, lightly pigmented hairs absorb laser energy less efficiently than thicker terminal hairs. When the laser energy is insufficient or improperly calibrated, instead of disabling the follicles, it may unintentionally stimulate them into an active growth phase.
This phenomenon is more likely to occur on areas such as the jawline, cheeks, upper lip, and sideburns, especially in individuals with hormonal fluctuations or undiagnosed conditions like PCOS. In some cases, even the peripheral areas adjacent to the treated zone may experience new hair growth, making facial treatments more complex than other body regions.
To reduce the risk of unwanted stimulation, it is critical to:
- Use laser devices suited for delicate facial zones (e.g., Diode or Nd:YAG for deeper, controlled targeting)
- Avoid treating vellus hair directly unless absolutely necessary
- Work with professionals experienced in treating fine facial hair across different skin types
If you have red, light-blonde, or grey hair, it’s also worth noting that laser may be less effective overall due to low melanin content. For more information on this, visit our detailed article on how laser hair removal works on red hair.
Which Laser Types are Most Likely to Trigger Hair Growth?
Certain laser types like Alexandrite, commonly effective on coarse and dark hair, have been reported in rare instances to stimulate growth in fine facial hair.
Diode and Nd:YAG lasers typically have lower stimulation risks, particularly for fine hairs and darker skin types, due to their deeper penetration and versatile profiles. However, individual outcomes can vary based on device settings, practitioner expertise, and personal hormonal factors. It’s also important to distinguish between laser devices and IPL systems, as they function differently and carry distinct risks. You can learn the nuances in our full IPL vs laser hair removal comparison guide.
Electrolysis as an Alternative for Paradoxical Hypertrichosis
For individuals who experience increased hair growth after laser hair removal—particularly in the form of paradoxical hypertrichosis—electrolysis offers a precise, targeted, and permanent solution. Unlike laser devices, which use light to heat multiple follicles at once, electrolysis destroys each hair follicle individually using a fine probe that delivers a controlled electric current. This direct approach avoids the risk of stimulating surrounding hair follicles, making it especially suitable for areas where laser has failed or caused unintended effects.
Electrolysis is commonly recommended in the following scenarios:
- Fine or light-colored facial hair that lasers cannot effectively treat
- Scattered regrowth after paradoxical hypertrichosis has occurred
- Isolated problem areas where precision is more valuable than speed
- Individuals with contraindications to laser, such as certain skin or hair types
The process requires multiple sessions due to the hair growth cycle and the need to treat each follicle during its active phase. If you’re considering switching to electrolysis after laser-related hair stimulation, you may wonder how long the full process takes. Learn more in our detailed guide on how many electrolysis sessions are typically needed.
While the treatment is slower compared to laser, electrolysis remains the only FDA-approved method for permanent hair removal and is frequently used in dermatological and aesthetic clinics to manage cases where laser treatments fall short.
How to Manage Paradoxical Hypertrichosis Effectively
If you’ve experienced increased hair growth post-laser:
- Immediately pause further laser sessions in affected areas. Besides paradoxical hypertrichosis, there are other temporary or rare side effects to be aware of. We’ve compiled a detailed overview of laser hair removal side effects to help you prepare for any potential reactions.
- Consult with a skin specialist to check for potential hormonal imbalances.
- Consider electrolysis as an alternative method for permanent hair removal.
- Use topical products recommended by skincare professionals, such as eflornithine cream, which may reduce hair growth temporarily.
How to Prevent Increased Hair Growth from Laser Procedures
Preventing paradoxical hypertrichosis involves careful planning and preparation:
- Choose clinics that use FDA-approved, appropriate laser types.
- Ensure the practitioner has extensive experience treating your specific hair and skin type.
- Discuss your complete medical and hormonal history openly with the technician before starting procedures.
Final Recommendations: Is Laser Hair Removal Still Worth It?
Despite the risks of paradoxical hypertrichosis, laser hair removal remains effective and safe for most individuals when correctly performed. Understanding potential risks and ensuring proper device selection significantly reduces the chances of unwanted outcomes. Always consult with qualified professionals and select FDA-approved technologies to safely achieve the desired smooth, hair-free results.

Our team consists of certified professionals with over 17 years of experience in laser hair removal, skincare, and personal care. With advanced training in diode laser, IPL, waxing, and skin health, we combine clinical precision with real-world expertise to deliver reliable, evidence-based guidance.
Every article is carefully created and reviewed by our experts to ensure safety, clarity, and scientific accuracy. Our work has helped thousands choose safe, effective hair removal solutions tailored to their unique needs.
Trusted expertise. Real results. That’s our promise.





